In mobile networks, the network switching system or NSS plays an important role in handling calls, text messages, and data services.
It manages how your phone talks to other phones, wherever you are. This system is part of the GSM Core Network, and it connects your phone with PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) and the Internet.
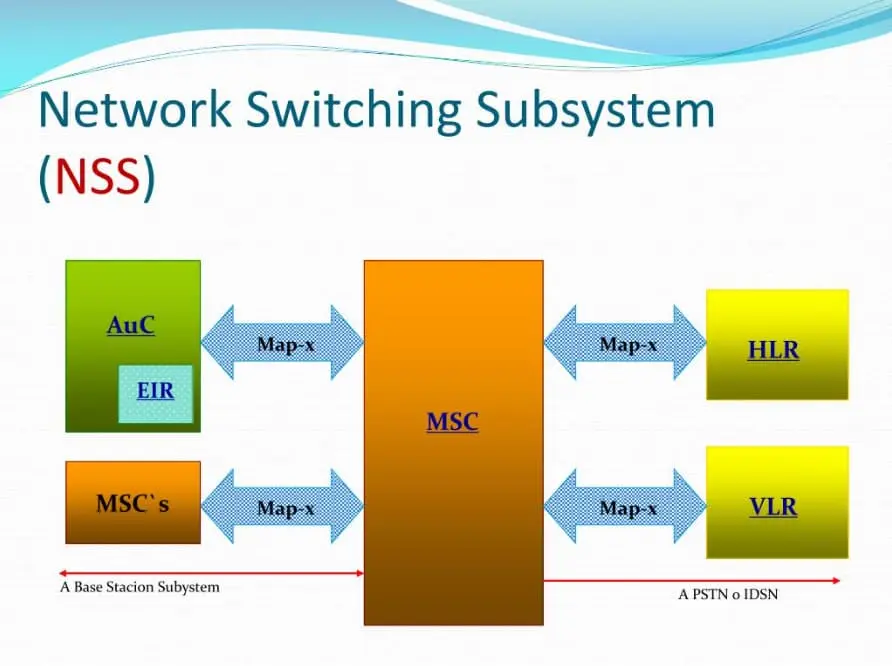
The network switching system works by using several important components that control switches, mobility, and security. These include MSC (Mobile Switching Center), CPR (Home Location Register), VLR (Visitor Register), and AUC (Authentication Center).
In this article, we will explain how each part works and how they all connect in a telecommunications network.
What Is the Network Switching Subsystem (NSS)?
Credit: allelcoelec.com
The Network Switching Subsystem is a group of network elements that makes it possible to handle calls and manage user location. It is a part of the GSM core network and is used by mobile phone operators to route calls, send texts, and manage the movement of phones across areas.
Since mobile users move from one location to another, the NSS is responsible for tracking and switching connections without interruptions.
The NSS originally relied on a circuit-based system to manage voice calls and SMS traffic. Later, it added support for packet-switched data using GPRS technology.
This allowed users to access services like internet browsing, MMS, and more advanced messaging. Today, both circuit switching (CS) and packet switching (PS) are essential parts of mobile communication.
| NSS Type | Functionality |
| Circuit Switching | Manages voice calls and traditional SMS |
| Packet Switching | Supports GPRS, MMS, and internet data services |
Key Components of NSS and Their Roles
1. Mobile Switching Center (MSC)
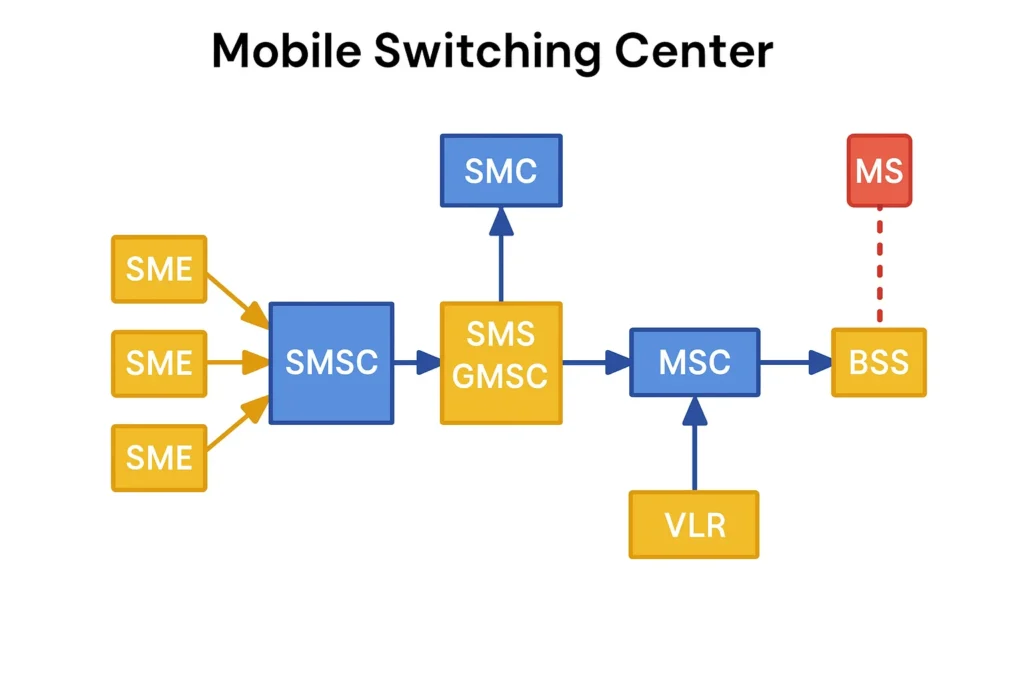
The mobile switch center is the most important part of NSS. It handles voicemail, call setup, text messages, and delivery procedures. It also controls charging and billing. The MSC links with various components across the network, including the Base Station Subsystem (BSS) and neighboring MSC units.
A special type called Gateway MSC (G-MSC) connects mobile networks with PSTN. The visited MSC (V-MSC) is used when outside the home network. Together, they ensure that conversations and messages reach the right person at the right time.
credit: emnify
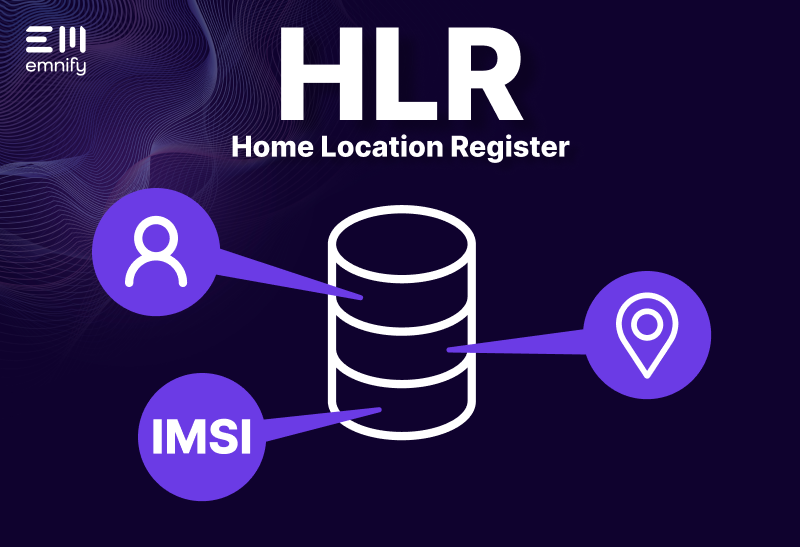
The HLR is a central database that stores permanent information about users. This includes the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) and Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Number (MSISDN). These are used to identify and locate mobile users.
The HLR also stores information about what services a user has, such as voicemail or data access. When a user turns on their phone, the HLR shares their location with the VLR and updates the system so calls and messages can be delivered.
| HLR Field | Description |
| IMSI | Unique subscriber identifier |
| MSISDN | Phone number linked to the SIM |
| Services | Data, call forwarding, and voicemail settings |
| Location | Area ID where the user is currently active |
3. Visitor Location Register (VLR)
The VLR is a temporary database. It stores user information when someone is visiting an area outside their home network. This helps reduce the load on the HLR and speeds up service delivery.
When a user enters a new area, the VLR updates its records and informs the HLR. It keeps track of your current Location Area Code (LAC) to help the system know where to send your calls and messages.
4. Authentication Center (AuC)
The Authentication Center (AuC) handles user verification to confirm SIM card authenticity. It generates a set of security codes, known as RAND, SRES, and Kc, using encryption algorithms (A3, A8, COMP128). These codes are sent to the MSC and used to confirm that a SIM card is valid.
| Component | Role |
| RAND | Random number for challenge |
| SRES | Signed response generated by SIM |
| Kc | Key used to encrypt user communications |
5. Equipment Identity Register (EIR)
The EIR is used to check the status of a mobile device using its IMEI (mobile equipment identity). If a phone is stolen or banned, its IMEI can be blacklisted in the EIR.
This helps network providers block stolen phones from using the service. It also improves security and reduces mobile fraud. In many systems, the Equipment Identity Register (EIR) is built directly into the Home Location Register (HLR) for streamlined access.
What are MSC and BSC in Telecom?
The Mobile Switching Center (MSC) handles switching tasks, such as setting up calls and forwarding SMS. As a key element of the core network, it interacts with internal databases and outside communication systems.
The Base Station Controller (BSC) manages the radio access network. It handles base stations and controls which cell tower your phone uses. The BSC works closely with the MSC to provide a smooth connection while you move between areas.
Core Functions of the Mobile Switching Center (MSC)
The MSC sets up and ends calls, handles SMS, and manages handover procedures when a user moves between areas. It connects users within the mobile network and with the PSTN.
It also helps in charging, stores billing records, and supports advanced services like call waiting, call forwarding, and conference calls. The MSC works alongside the Short Message Service Center (SMSC) to manage the transfer of text messages.
Read Also: A Guide to AI SaaS Product Classification Criteria
The MSC and HLR work together to identify users and send calls or messages to the correct place. When a call comes in, the MSC checks the HLR to find out where the user is located.
The HLR responds with the user’s current area, and the MSC sends the call to that area using the VLR. This teamwork is what allows mobile communication to work even when users move around.
MSC in Action: Role During Handover
When a mobile user moves during a call, the handover procedure allows the call to continue without dropping. The MSC handles this by passing control to another BSC or MSC, depending on where the user moves.
Handovers can occur inside a single MSC, across multiple MSCs, or even between different networks, depending on user movement. The MSC makes fast decisions to maintain call quality.
Real-World Examples of MSC Implementation
In the United States, telecom providers like AT&T and Verizon use centralized MSC architectures for cities and regional MSCs for rural areas. This setup helps balance load and improve performance.
Some MSC servers (MSC-S / MSS) are placed in data centers with Media Gateways (MGW) distributed across locations. This design supports large-scale switching and connects with both mobile and fixed-line networks.
Interconnection with Other GSM Network Elements
The MSC connects with several systems, including the BSS, HLR, VLR, AuC, SMSC, and the PSTN. These connections use the MAP protocol and 3GPP standards.
This setup ensures that the NSS can deliver messages, calls, and authentication in real-time. It also supports handovers and location updates.
Other Support Functions in NSS
Billing Center (BC)
The Billing Center (BC) gathers usage data from both the MSC and VLR to generate accurate billing information. It processes them into billing files and sends them to the customer’s account. This includes local, international, and roaming charges.
Multimedia Messaging Service Center (MMSC)
The MMSC handles sending and receiving multimedia messages like pictures, audio, and video. It works alongside the MSC and GPRS core to deliver content to mobile devices.
Voicemail System (VMS)
The VMS (Voicemail System) records and stores voice messages when a user is unavailable. It notifies users when a message is waiting and lets them listen to or delete it.
Lawful Interception Capabilities
The Lawful Interception / CALEA system allows authorities to monitor calls with proper approval. The MSC provides access to live call data and SMS when required by law.
This is used in criminal investigations or national security cases and follows strict procedures.
Read Also: How to Bypass LockDown Browser in 2025?
Security and Encryption within NSS
Security is managed using the AuC and MSC, which work together to protect communication. They generate and use an encryption key (Kc) to secure voice, SMS, and data traffic.
This process uses the A3/A8 algorithm and avoids sending the Ki secret key over the air. Before granting access, the system checks the calculated authentication values to confirm the user’s identity.
Evolution of MSC in Modern Networks (MSC-S and MGW)
In newer systems, the MSC has evolved into a Mobile Softswitch (MSS), separating the control and user layers. This model uses Media Gateways (MGW) to carry the actual voice and data.
With the 3GPP Release 4, this allows telecom operators to scale networks, reduce costs, and support modern features like VoIP and IP-based switching.
Conclusion
The Network Switching Subsystem is essential to mobile communication. With core components like MSC, HLR, and VLR, it manages switching, security, and services. Each part plays a key role in keeping your phone connected and working properly.
As networks shift to 4G and 5G, many of these components continue to operate behind the scenes. Understanding how the Network Switching Subsystem works gives a clearer picture of how modern mobile networks keep us all connected.